Recently, the Deep Sea Science and Engineering Research Team of the Institute of Deep Sea Science and Engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the University of China University, the University of Petroleum (East China), and the University of Barcelona in Spain, the study revealed a fracture belt that is currently on the south of the South China Sea -land slope fracturebring.Related results online published in “Ocean and Petroleum Geology” (Marine and Petroleum GeologyTo.

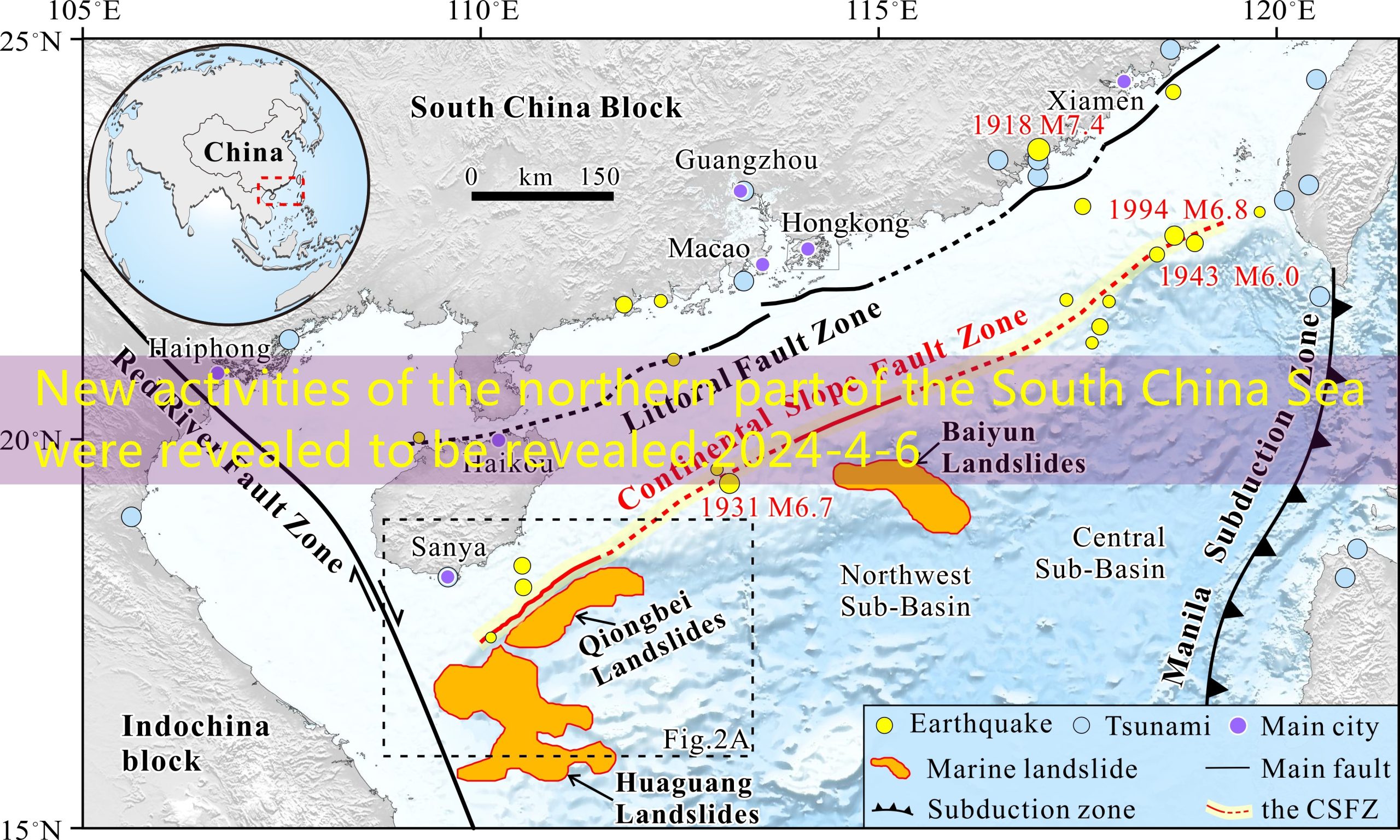
The distribution map of the fracture belt in the north of the South China Sea (the littoral fault zone; the Lupo broken belt: Continental Slope Fault Zone).Interviewee confession
The first author of the paper, the Institute of Deep Sea Science and Engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the joint training doctoral student Zeng Fanchang, a doctoral student at Sun Yat-sen University, said that the seabed fracture activities will not only trigger the earthquake, but also often trigger the sea floor landslide-tsunami disaster chain.More destructive.The spatial distribution, structural characteristics, and latest activity of the underwater activity layer are key parameters of marine geological disaster assessment.
The research uses high -precision multi -channel earthquake, heavy magnetic, and underwater terrain data. It systematically studies the activity structure of the deep -water area in the northern part of the South China Sea, and reveals the spatial distribution, structural characteristics, and latest activity of the land -sloping zone.The research results show that the sloping belt of the land is a activity fracture belt with a length of about 1100 km in the nearby land slope zip zone.The flat/section of the Lupo broken belt (Qiong south section) presents the structural characteristics of positive and slippery.Broken analysis and growth index showed that Lupo’s broken belt (Qiong south section) has occurred many activities since the fourth period of the evening.Combined with the characteristics of the underwater landforms today, it is believed that the slopes of the Lupo may be further moved in the future, and may trigger the effects of the underwater earthquake-landslide-tsunami disaster chain effect, which is dangerous for geological disasters.
Wang Dawei, author of the common communication author and researcher at the Institute of Deep Sea Science and Engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, pointed out that the study revealed the specific distribution, geometric structure, and latest activity of the northern northern part of my country, providing basic data for geological disaster assessment in my country.
The above research work has been funded by projects such as national key research and development plans, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the introduction of talent innovation and entrepreneurship team projects in Guangdong Province.